Page 5 - LN-CH-12
P. 5
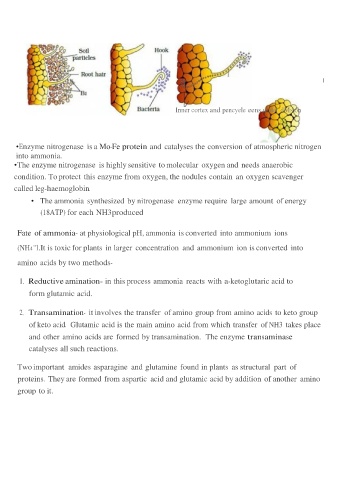
nfecuon l
thread
ctena conuuntng
bacteria
{al Inner cortex and pencyele eens under dMston
• Enzyme nitrogenase is a Mo-Fe protein and catalyses the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen
into ammonia.
• The enzyme nitrogenase is highly sensitive to molecular oxygen and needs anaerobic
condition. To protect this enzyme from oxygen, the nodules contain an oxygen scavenger
called leg-haemoglobin.
• The ammonia synthesized by nitrogenase enzyme require large amount of energy
(18ATP) for each NH3produced
Fate of ammonia- at physiological pH, ammonia is converted into ammonium ions
(NH4"l.It is toxic for plants in larger concentration and ammonium ion is converted into
amino acids by two methods-
1. Reductive amination- in this process ammonia reacts with a-ketoglutaric acid to
form glutamic acid.
2. Transamination- it involves the transfer of amino group from amino acids to keto group
of keto acid. Glutamic acid is the main amino acid from which transfer of NH3 takes place
and other amino acids are formed by transamination. The enzyme transaminase
catalyses all such reactions.
Two important amides asparagine and glutamine found in plants as structural part of
proteins. They are formed from aspartic acid and glutamic acid by addition of another amino
group to it.