Page 13 - LN-cH-11
P. 13
approximately 32 years by diffusion alone.
In large and complex organisms, sites of production or absorption and sites of
storage are far away from one another thus, the substances to be transferred have to
follow a long path and move across very large distances.
Hence, some special long distance transport systems are necessary in order to
transfer substances across long distances at much faster rate.
The movement of water, minerals and food across long distances is generally done
by a mass or bulk flow system, which operates due to difference between the
pressure of two points, i.e., the source and the sink. The substances whether
dissolved or suspended in solution, are carried at a same speed. Such a movement
is different from diffusion where different substances move independent of each
other depending upon concentration gradients of their own. Mass or bulk flow
movement occurs through vascular tissues, xylem and phloem of plants. The bulk
movement of substances through conducting or vascular tissues of plant is called
translocation.
There are generally two types of vascular tissues in plants which are responsible
for translocation
(i) Xylem It is responsible for translocation of water with mineral salts, some organic
nitrogen and hormones mainly from roots to aerial parts of plants.
(ii) Phloem It is responsible for translocation of organic and inorganic substances
from leaves to other parts of the plant. Bulk flow can operate either due to positive
hydrostatic pressure gradient (like a garden hose) as in phloem or a negative
hydrostatic pressure gradient (like suction through a straw) as in xylem.
Absorption of Water by Plants
Plants absorb water through roots. However, the area of young roots where most
absorption of water and minerals takes place is root hair zone. Root hairs are thin
walled, slender extension of root epidermal cell present at the tip of the roots in
millions. These are very delicate structure, which do not last for more than days or a
week. They have very sticky walls that help in tight adhesion to the soil particles.
Tracheids and trachea of xylem transport water in plants.
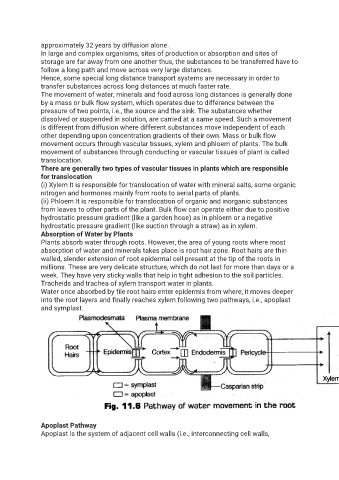
Water once absorbed by file root hairs enter epidermis from where, it moves deeper
into the root layers and finally reaches xylem following two pathways, i.e., apoplast
and symplast.
Apoplast Pathway
Apoplast is the system of adjacent cell walls (i.e., interconnecting cell walls,