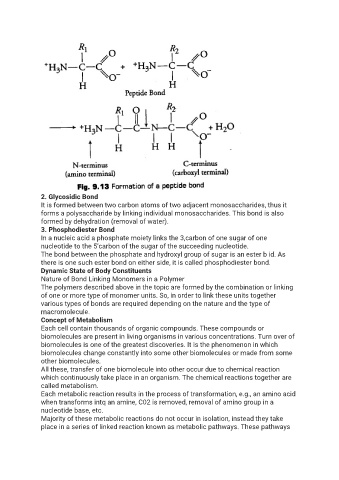
Page 19 - Lesson Notes - Biomolecules 1
P. 19
2. Glycosidic Bond
It is formed between two carbon atoms of two adjacent monosaccharides, thus it
forms a polysaccharide by linking individual monosaccharides. This bond is also
formed by dehydration (removal of water).
3. Phosphodiester Bond
In a nucleic acid a phosphate moiety links the 3,carbon of one sugar of one
nucleotide to the 5’carbon of the sugar of the succeeding nucleotide.
The bond between the phosphate and hydroxyl group of sugar is an ester b id. As
there is one such ester bond on either side, it is called phosphodiester bond.
Dynamic State of Body Constituents
Nature of Bond Linking Monomers in a Polymer
The polymers described above in the topic are formed by the combination or linking
of one or more type of monomer units. So, in order to link these units together
various types of bonds are required depending on the nature and the type of
macromolecule.
Concept of Metabolism
Each cell contain thousands of organic compounds. These compounds or
biomolecules are present in living organisms in various concentrations. Turn over of
biomolecules is one of the greatest discoveries. It is the phenomenon in which
biomolecules change constantly into some other biomolecules or made from some
other biomolecules.
All these, transfer of one biomolecule into other occur due to chemical reaction
which continuously take place in an organism. The chemical reactions together are
called metabolism.
Each metabolic reaction results in the process of transformation, e.g., an amino acid
when transforms intq an amine, C02 is removed, removal of amino group in a
nucleotide base, etc.
Majority of these metabolic reactions do not occur in isolation, instead they take
place in a series of linked reaction known as metabolic pathways. These pathways