Page 18 - Lesson Notes-Morphologyof flowering plant
P. 18
of ovary.
These positions may be of three types
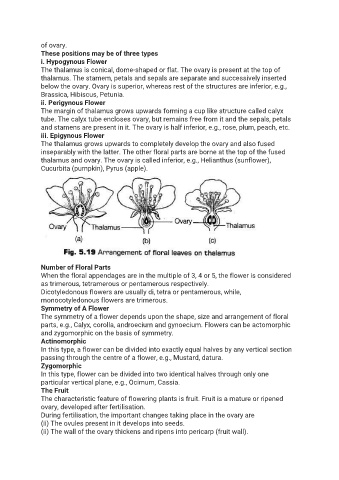
i. Hypogynous Flower
The thalamus is conical, dome-shaped or flat. The ovary is present at the top of
thalamus. The stamem, petals and sepals are separate and successively inserted
below the ovary. Ovary is superior, whereas rest of the structures are inferior, e.g.,
Brassica, Hibiscus, Petunia.
ii. Perigynous Flower
The margin of thalamus grows upwards forming a cup like structure called calyx
tube. The calyx tube encloses ovary, but remains free from it and the sepals, petals
and stamens are present in it. The ovary is half inferior, e.g., rose, plum, peach, etc.
iii. Epigynous Flower
The thalamus grows upwards to completely develop the ovary and also fused
inseparably with the latter. The other floral parts are borne at the top of the fused
thalamus and ovary. The ovary is called inferior, e.g., Helianthus (sunflower),
Cucurbita (pumpkin), Pyrus (apple).
Number of Floral Parts
When the floral appendages are in the multiple of 3, 4 or 5, the flower is considered
as trimerous, tetramerous or pentamerous respectively.
Dicotyledonous flowers are usually di, tetra or pentamerous, while,
monocotyledonous flowers are trimerous.
Symmetry of A Flower
The symmetry of a flower depends upon the shape, size and arrangement of floral
parts, e.g., Calyx, corolla, androecium and gynoecium. Flowers can be actomorphic
and zygomorphic on the basis of symmetry.
Actinomorphic
In this type, a flower can be divided into exactly equal halves by any vertical section
passing through the centre of a flower, e.g., Mustard, datura.
Zygomorphic
In this type, flower can be divided into two identical halves through only one
particular vertical plane, e.g., Ocimum, Cassia.
The Fruit
The characteristic feature of flowering plants is fruit. Fruit is a mature or ripened
ovary, developed after fertilisation.
During fertilisation, the important changes taking place in the ovary are
(ii) The ovules present in it develops into seeds.
(ii) The wall of the ovary thickens and ripens into pericarp (fruit wall).