Page 2 - 3.Home_Assignment_II_(Worksheet_2)_Reproductive_health
P. 2
Q.6 (a) What is ovulation?
(b) How many ovaries are present in a human female? Name the hormones
secreted by them.
(c) State the changes that take place in the uterus when –
(i) Implantation of embryo has occurred.
(ii) Female gamete/egg is not fertilised.
Q.7 (a) What are the benefits of using mechanical barrier during sexual act?
(b) What is the nature of oral pills being used as contraceptive devices?
Q.8 (a) Name the following parts –
(i) Part where fertilisation takes place
(ii) Small sac-like muscular structure that encloses testes.
(iii) Birth canal
(iv) The organ where foetus develops during gestation
(v) Structure associated with mating
(vi) Primary sex organs in man and woman
(b) Define sexually transmitted disease with two examples.
(c) Name a contraceptive device that is used to avoid pregnancy as well as
STD. Do you think, vasectomy and tubectomy serve both the purposes?
Whether these methods are reversable or irreversible?
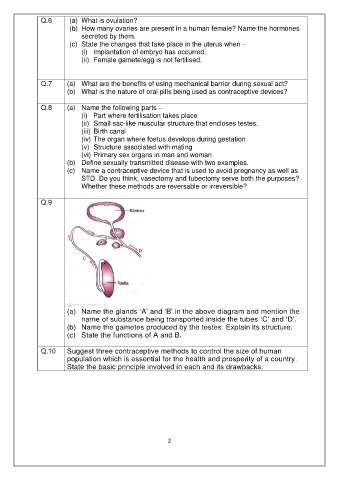
Q.9
(a) Name the glands ‘A’ and ‘B’ in the above diagram and mention the
name of substance being transported inside the tubes ‘C’ and ‘D’.
(b) Name the gametes produced by the testes. Explain its structure.
(c) State the functions of A and B.
Q.10 Suggest three contraceptive methods to control the size of human
population which is essential for the health and prosperity of a country.
State the basic principle involved in each and its drawbacks.
2