Page 2 - HA1
P. 2
(a) Pollination, fertilization, seedling, embryo
(b) Seedling, embryo, fertilization, pollination
(c) Pollination, fertilization, embryo, seedling
(d) Embryo, seedling, pollination, fertilization
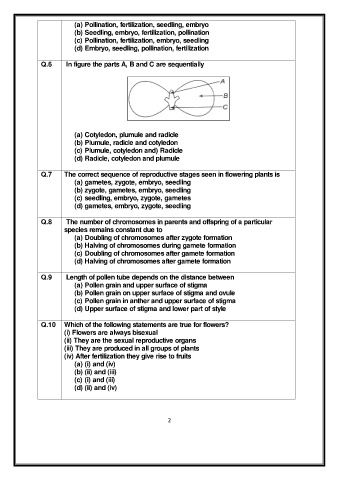
Q.6 In figure the parts A, B and C are sequentially
(a) Cotyledon, plumule and radicle
(b) Plumule, radicle and cotyledon
(c) Plumule, cotyledon and) Radicle
(d) Radicle, cotyledon and plumule
Q.7 The correct sequence of reproductive stages seen in flowering plants is
(a) gametes, zygote, embryo, seedling
(b) zygote, gametes, embryo, seedling
(c) seedling, embryo, zygote, gametes
(d) gametes, embryo, zygote, seedling
Q.8 The number of chromosomes in parents and offspring of a particular
species remains constant due to
(a) Doubling of chromosomes after zygote formation
(b) Halving of chromosomes during gamete formation
(c) Doubling of chromosomes after gamete formation
(d) Halving of chromosomes after gamete formation
Q.9 Length of pollen tube depends on the distance between
(a) Pollen grain and upper surface of stigma
(b) Pollen grain on upper surface of stigma and ovule
(c) Pollen grain in anther and upper surface of stigma
(d) Upper surface of stigma and lower part of style
Q.10 Which of the following statements are true for flowers?
(i) Flowers are always bisexual
(ii) They are the sexual reproductive organs
(iii) They are produced in all groups of plants
(iv) After fertilization they give rise to fruits
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
2