Page 3 - 3.LESSON NOTES-(CH-2 PH OF ACIDS & BASES)
P. 3
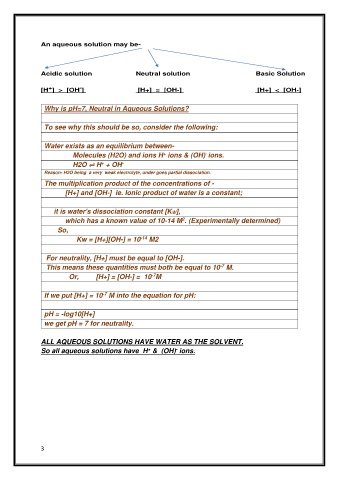
An aqueous solution may be-
Acidic solution Neutral solution Basic Solution
-
+
[H ] > [OH ] [H+] = [OH-] [H+] < [OH-]
Why is pH=7, Neutral in Aqueous Solutions?
To see why this should be so, consider the following:
Water exists as an equilibrium between-
Molecules (H2O) and ions H ions & (OH) ions.
-
+
+
H2O ⇌ H + OH -
Reason- H2O being a very weak electrolyte, under goes partial dissociation.
The multiplication product of the concentrations of -
[H+] and [OH-] ie. Ionic product of water is a constant;
it is water's dissociation constant [KW],
2
which has a known value of 10-14 M . (Experimentally determined)
So,
Kw = [H+][OH-] = 10 M2
-14
For neutrality, [H+] must be equal to [OH-].
-7
This means these quantities must both be equal to 10 M.
-7
Or, [H+] = [OH-] = 10 M
-7
If we put [H+] = 10 M into the equation for pH:
pH = -log10[H+]
we get pH = 7 for neutrality.
ALL AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS HAVE WATER AS THE SOLVENT.
-
+
So all aqueous solutions have H & (OH) ions.
3