Page 1 - Lesson note refraction through glass slab
P. 1
SAI INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL
PHYSICS
CLASS X
Chapter: LIGHT(REFLECTION & REFRACTION)
MODULE-28
LESSON NOTES: refraction through glass slab
The ray of light bends twice. First time when it enters from air to the glass slab, it
bends towards the normal, i.e., from rarer medium to denser medium. Second time,
when the ray moves out from the glass slab to air, it bends away from the normal,
i.e., it moves from denser medium to rarer medium.
Prove that the incident angle and the emergent angle in a rectangular glass
slab are equal
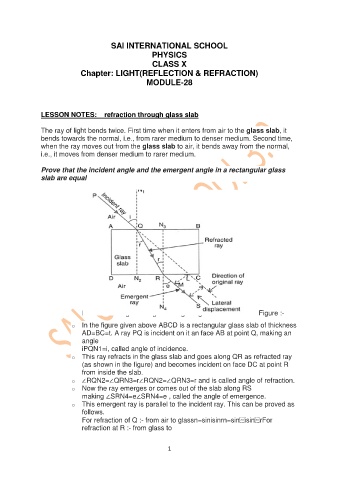
Refraction of light through rectangular glass slab Figure :-
o In the figure given above ABCD is a rectangular glass slab of thickness
AD=BC=t. A ray PQ is incident on it an face AB at point Q, making an
angle
iPQN1=i, called angle of incidence.
o This ray refracts in the glass slab and goes along QR as refracted ray
(as shown in the figure) and becomes incident on face DC at point R
from inside the slab.
o ∠RQN2=∠QRN3=r∠RQN2=∠QRN3=r and is called angle of refraction.
o Now the ray emerges or comes out of the slab along RS
making ∠SRN4=e∠SRN4=e , called the angle of emergence.
o This emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray. This can be proved as
follows.
For refraction of Q :- from air to glassn=sinisinrn=sinisinrFor
refraction at R :- from glass to
1