Page 3 - Lesson note reflection through spherical mirror
P. 3
Principle focus and focal length of a Spherical Mirrors
For understanding about principle focus and focus length of a spherical mirror
first consider the figure given below
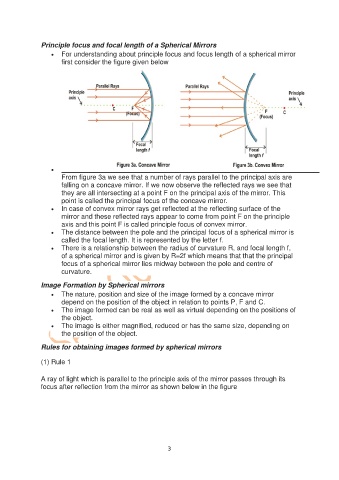
From figure 3a we see that a number of rays parallel to the principal axis are
falling on a concave mirror. If we now observe the reflected rays we see that
they are all intersecting at a point F on the principal axis of the mirror. This
point is called the principal focus of the concave mirror.
In case of convex mirror rays get reflected at the reflecting surface of the
mirror and these reflected rays appear to come from point F on the principle
axis and this point F is called principle focus of convex mirror.
The distance between the pole and the principal focus of a spherical mirror is
called the focal length. It is represented by the letter f.
There is a relationship between the radius of curvature R, and focal length f,
of a spherical mirror and is given by R=2f which means that that the principal
focus of a spherical mirror lies midway between the pole and centre of
curvature.
Image Formation by Spherical mirrors
The nature, position and size of the image formed by a concave mirror
depend on the position of the object in relation to points P, F and C.
The image formed can be real as well as virtual depending on the positions of
the object.
The image is either magnified, reduced or has the same size, depending on
the position of the object.
Rules for obtaining images formed by spherical mirrors
(1) Rule 1
A ray of light which is parallel to the principle axis of the mirror passes through its
focus after reflection from the mirror as shown below in the figure
3