Page 1 - LN
P. 1
LESSON NOTES
Human Ear
The ear is a sensitive organ of the human body. It is mainly concerned with
detecting, transmitting and transducing sound. Maintaining a sense of balance is
another important function performed by the human ear.
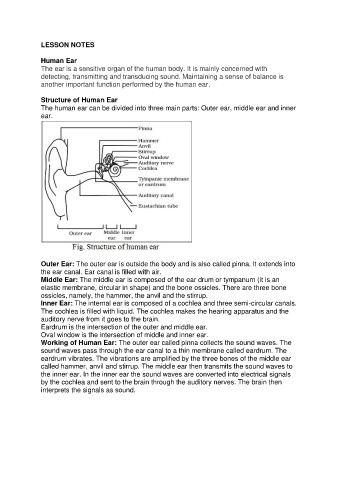
Structure of Human Ear
The human ear can be divided into three main parts: Outer ear, middle ear and inner
ear.
Outer Ear: The outer ear is outside the body and is also called pinna. It extends into
the ear canal. Ear canal is filled with air.
Middle Ear: The middle ear is composed of the ear drum or tympanum (it is an
elastic membrane, circular in shape) and the bone ossicles. There are three bone
ossicles, namely, the hammer, the anvil and the stirrup.
Inner Ear: The internal ear is composed of a cochlea and three semi-circular canals.
The cochlea is filled with liquid. The cochlea makes the hearing apparatus and the
auditory nerve from it goes to the brain.
Eardrum is the intersection of the outer and middle ear.
Oval window is the intersection of middle and inner ear.
Working of Human Ear: The outer ear called pinna collects the sound waves. The
sound waves pass through the ear canal to a thin membrane called eardrum. The
eardrum vibrates. The vibrations are amplified by the three bones of the middle ear
called hammer, anvil and stirrup. The middle ear then transmits the sound waves to
the inner ear. In the inner ear the sound waves are converted into electrical signals
by the cochlea and sent to the brain through the auditory nerves. The brain then
interprets the signals as sound.