Page 1 - Simple Queries in SQL
P. 1
MySQL and Simple Queries in SQL
Why MySQL
Open source and freely available
Uses SQL
Can be easily downloaded from the site www.mysql.org
MySQL database system works upon client/server architecture (Client makes request to the
Server, Server access database and serves the request)
It constitutes a MySQL server which runs on a machine containing the databases and client
connect to the server over a network
My SQL is a multi-user database system
Advantages of MySQL
1) Reliability and performance
2) Easy to use
3) Free and supports SQL
4) Portable/multiplatform support
5) Datatypes
6) Integrity checks
7) Scalability and limits (Has powerful processing capabilities and can handle large databases
containing 60,000 tables and more then 50 million rows.
8) Security (by username and password authentication)
9) Connectivity (Client can connect to MySQL server using several protocols)
SQL Datatypes
Each value manipulated by SQL Database has a data type.
A data type specifies the possible values for a variable/identifier, the operations that can be
performed on that type and the way the values of that type are stored.
The data type of a value associates a fixed set of properties with the value. In SQL there are three
main data types:
• Number
• Date
• Character/String
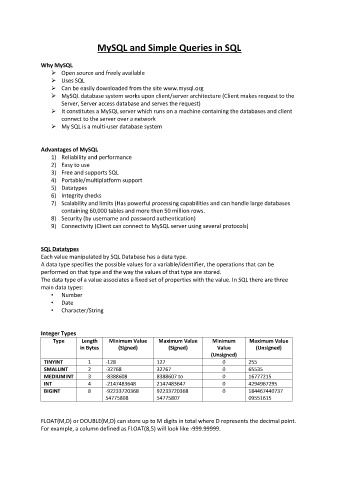
Integer Types
Type Length Minimum Value Maximum Value Minimum Maximum Value
in Bytes (Signed) (Signed) Value (Unsigned)
(Unsigned)
TINYINT 1 -128 127 0 255
SMALLINT 2 -32768 32767 0 65535
MEDIUMINT 3 -8388608 8388607 to 0 16777215
INT 4 -2147483648 2147483647 0 4294967295
BIGINT 8 -92233720368 92233720368 0 184467440737
54775808 54775807 09551615
FLOAT(M,D) or DOUBLE(M,D) can store up to M digits in total where D represents the decimal point.
For example, a column defined as FLOAT(8,5) will look like -999.99999.