Page 1 - DATA STRUCTURE-LISTS
P. 1
DATA STRUCTURE
(LISTS)
A data structure is a group of data which can be processed as a single unit. This group of
data may be of similar or dissimilar data types. A DS has well defined operations, behaviour
and properties.
Data Structures are very useful while programming because they allow processing of the
entire group of data as a single unit. This makes managing of data simpler. The simplest
form of data structure is an array which combines finite data of same data type.
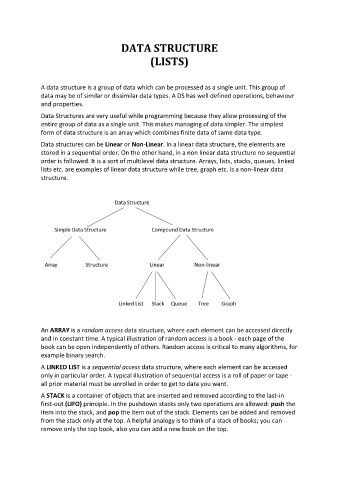
Data structures can be Linear or Non-Linear. In a linear data structure, the elements are
stored in a sequential order. On the other hand, in a non linear data structure no sequential
order is followed. It is a sort of multilevel data structure. Arrays, lists, stacks, queues, linked
lists etc. are examples of linear data structure while tree, graph etc. is a non-linear data
structure.
An ARRAY is a random access data structure, where each element can be accessed directly
and in constant time. A typical illustration of random access is a book - each page of the
book can be open independently of others. Random access is critical to many algorithms, for
example binary search.
A LINKED LIST is a sequential access data structure, where each element can be accessed
only in particular order. A typical illustration of sequential access is a roll of paper or tape -
all prior material must be unrolled in order to get to data you want.
A STACK is a container of objects that are inserted and removed according to the last-in
first-out (LIFO) principle. In the pushdown stacks only two operations are allowed: push the
item into the stack, and pop the item out of the stack. Elements can be added and removed
from the stack only at the top. A helpful analogy is to think of a stack of books; you can
remove only the top book, also you can add a new book on the top.